For more information about product availability globally, please click below.
OrbusNeich Medical Co. Ltd.:
→APAC (Asia-Pacific)
→EMEA (Europe, Middle East, Africa)
ON has exclusive distribution rights in the following countries: Czech Republic, Slovakia, Egypt, Hong Kong, Italy, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Malaysia, Singapore, Spain, Switzerland, and United Arab Emirates; ON has non-exclusive distribution rights in Austria, France, Germany, and the Netherlands.
Medikit Co., Ltd:
→Japan
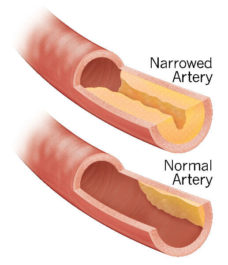
In November 2016, Cardiovascular Systems, Inc. (CSI) announced that Medikit, Co., Ltd. signed an exclusive distribution agreement to sell its coronary and peripheral Orbital Atherectomy Systems in Japan.
PT. Revass Utama Medika:
→Indonesia
In February 2021, Cardiovascular Systems, Inc. (CSI) announced that PT. Revass Utama Medika signed an exclusive distribution agreement to sell its coronary and peripheral Orbital Atherectomy Systems in Indonesia.
Bio-Excel (Australia) Pty. Ltd.:
→Australia
In March 2021, Cardiovascular Systems, Inc. (CSI) announced that Bio-Excel Co. Ltd. signed an exclusive distribution agreement to sell its coronary and peripheral Orbital Atherectomy Systems in Australia.
RSK Medical Inc.
→Canada
In April 2021, Cardiovascular Systems, Inc. (CSI) announced that RSK Medical Inc. signed an exclusive sales agent agreement to sell its coronary and peripheral Orbital Atherectomy Systems in Canada.
CardiRad Group
→Nordics
In August 2021, Cardiovascular Systems, Inc. (CSI) announced that CardiRad Group signed an exclusive distribution agreement to sell its coronary and peripheral Orbital Atherectomy Systems in Finland, Sweden, Norway and Denmark.
ProCardia Medical Sp. z o. o.
→Poland
In September 2021, Cardiovascular Systems, Inc. (CSI) announced that ProCardia Medical Sp. z o. o. signed an exclusive distribution agreement to sell its coronary and peripheral Orbital Atherectomy Systems in Poland.
Vascular Perspectives Ltd.
→U.K.
In August 2021, Cardiovascular Systems, Inc. (CSI) announced that Vascular Perspectives Ltd. signed an exclusive sales agent agreement to sell its coronary and peripheral Orbital Atherectomy Systems in U.K.
SISK Healthcare/Synapse Medical
→Ireland
In September 2021, Cardiovascular Systems, Inc. (CSI) announced that SISK Healthcare UC Trading as Synapse Medical signed an exclusive distribution agreement to sell its coronary and peripheral Orbital Atherectomy Systems in Ireland.